1. 상속(inheritance)
1.1 상속의 정의와 장점

- 적은 양의 코드로 새로운 클래스 작성 가능, 추가 및 변경이 용이하다
상속받는법
class Parent{}
class Child extends Parent{
//...
}
조상 클래스 - 부모(parent) 클래스, 상위(super) 클래스, 기반(base) 클래스
자손 클래스 - 자식(child) 클래스, 하위(sub) 클래스, 파생된(derived) 클래스
상속계층도
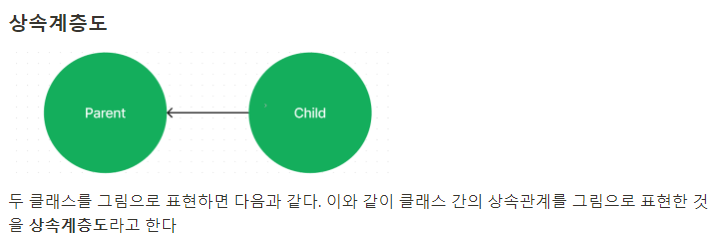
- 클래스 Parent 와 Child의 다이어그램

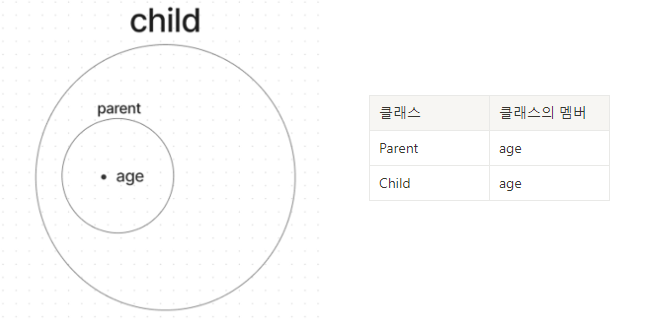
- Parent 클래스에 age라는 정수형 멤버변수를 추가한다면?
class Parent{
int age;
}
class Child extends Parent {}
→ 자손 클래스는 조상 클래스의 멤버를 모두 상속받기 때문에, Child 클래스는 자동적으로 age라는 멤버변수가 추가된 것과 같은 효과를 얻는다.
- 반대로 자손인 Child 클래스에 새로운 멤버로 play() 메서드를 추가해보자

class Parent{
int age;
}
class Child extends Parent{
void.play() {
System.out.println("놀자 ~")
}
}
→ Child클래스에 새로운 코드가 추가되어도 조상인 Parent 에 아무런 영향을 받지 않는다.

- Parent 클래스로부터 상속받는 Child2 클래스를 작성하면?
class Parent {}
class Child1 extends Parent{}
class Child2 extends Parent{}
→ 클래스 간의 관계에서 형제관계 같은 것은 없다. 부모와 자식 ,즉 상속 관계만이 존재할 뿐이다.
만일 child 1 클래스와 child 2 클래스에 공통적으로 추가되어야 하는 멤버가 있따면 공통조상인 Parent 클래스에 추가하는 것이 좋다. (코드의 중복성 제거)
- Grand child 새로운 계층 추가를 한다면?
class Parent {}
class Child1 extends Parent{}
class Child2 extends Parent{}
class GrandChild extends Child1{}
→ 자손 클래스는 조상 클래스의 모든 멤버를 물려받으므로 GrandChild 클래스는 Child1과 Parent 클래스의 모든 멤버를 물려받는다. Parent 클래스와 GrandChild클래스는 간접적인 상속관계에 있다고 할 수 있다.
- 예제 CaptionTv
class Tv{
boolean power; // 전원 상태
int channel; // 채널
void power() { power = !power;}
void channelUp() { ++channel; }
void channelDown() { --channel; }
}
class CaptionTv extends Tv{
boolean caption; // 캡션상태(on/off)
void displayCaption(String text) {
if (caption) { //캡션 상태가 on(true)일 때만 text를 보여준다.
System.out.println(text);
}
}
}
class CaptionTvtest{
public static void main(String[] args) {
CaptionTv ctv = new CaptionTv();
ctv.channel = 10; // 조상 클래스로부터 상속받은 멤버
ctv.channelUp(); // 조상 클래스로부터 상속받은 멤버
System.out.println(ctv.channel);
ctv.displayCaption("Hello World"); // caption이 off이기 때문에 반응하지 않는다
ctv.caption = true;
ctv.displayCaption("Hello World"); // caption이 on이기 때문에 출력한다
}
}

1.2 클래스간의 관계 - 포함관계
- 클래스간의 포함 관계를 맺어주는 것은 한 클래스의 멤버변수로 다른 클래스의 찹조변수를 선언하는 것을 뜻한다.
예시
- 원을 표현하기 위한 Circle클래스를 다음과 같이 작성한다
class Cicle {
int x; // 원점의 x좌표
int y; // 원점의 y좌표
int r; // 반지름(radius)
}
- 좌표상의 한 점을 다루기 위해 Point 클래스가 다음과 같이 작성되었다고 하자
class Point{
int x;
int y;
}
- Point 클래스를 재사용해서 Circle 클래스를 작성한다면 다음과 같이 할 수 있다. (좌 → 우)
class Cicle {
int x; // 원점의 x좌표
int y; // 원점의 y좌표
int r; // 반지름(radius)
}
class Cicle {
Point C = new Point(); // 원점
int r; // 반지름(radius)
}
1.3 클래스간의 관계 결정하기
- 클래스를 작성하는데 있어서 상속 관계를 맺어줄 것인지 포함관계를 맺어줄 것인지 결정하는 것은 때때로 혼돈스러울 수 있다.
class Circle {
Point C = new Point();
int r;
}
class Circle extend Point{
int r;
}
- 그럴 때는 다음과 같이 구분하면 관계가 명확해진다
원은 점이다 - Circle is a Point
원은 점을 가지고 있다 - Circle has a Point

예제 7.2
class DrawShape {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Point[] p = { new Point(100, 100),
new Point(140, 50),
new Point(200, 100)
};
Triangle t = new Triangle(p);
Circle c = new Circle(new Point(150, 150), 50);
t.draw();
c.draw();
}
}
class Shape{
String color = "black";
void draw(){
System.out.printf("[color=%s]%n", color);
}
}
class Point{
int x;
int y;
Point(int x, int y){
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
Point() {
this(0,0);
}
String getXY(){
return "("+x+","+y+")"; // x와 y의 값을 문자열로 반환
}
}
class Circle extends Shape{
Point center;
int r;
Circle(){
this(new Point(0, 0), 100);
}
Circle(Point center, int r){
this.center = center;
this.r = r;
}
void draw() { //원의 정보를 출력
System.out.printf("[center=(%d, %d), r=%d, color=%s]%n", center.x, center.y, r, color);
}
}
class Triangle extends Shape{
Point[] p = new Point[3];
Triangle(Point[] p){
this.p = p;
}
void draw(){ // 삼각형의 정보를 출력
System.out.printf("[p1=%s, p2=%s, p3=%s, color=%s]", p[0].getXY(), p[1].getXY(), p[2].getXY(), color);
}
}
class Shape{
String color = "black";
void draw(){
System.out.printf("[color=%s]%n", color);
}
}
// Circle 클래스에도 draw()가 정의되어 있다.
void draw() { //원의 정보를 출력
System.out.printf("[center=(%d, %d), r=%d, color=%s]%n", center.x, center.y, r, color);
}
조상 클래스에 정의된 메서드르 자손 클래스에 정의했을 경우, 자손 클래스 메서드가 호출된다. 이를 오버라이딩이라하며 추후에 배운다.
- 코드 중 의문점? Circle 인스턴스 생성 문장
Circle c = new Circle(new Point(150, 150), 50);
- 이문장은 아래의 두 문장을 하나로 합쳐놓은 것이다.
Point **p** = new Point(150, 150);
Circle c = new Circle(**p**, 50);
1.4 단일 상속(single inheritance)
class TVCR extends TV, VCR{} // 에러. 조상은 하나만 허용된다.
- C++와 달리 자바에서는 단일상속만을 허용한다.
- 다중상속
- 복합적 기능을 가진 클래스를 쉽게 작성 가능
- 그러나 클래스간의 관계가 복잡해진다
- 서로 다른 클래스로부터 상속받은 멤버의 이름이 같은 경우 구별할 수 없다
- 단일 상속
- 하나의 조상 클래스만을 상속받을 수 있다.
- 코드가 명확해지고, 더욱 신뢰할 수 있다.
1.5 Object 클래스 - 모든 클래스의 조상

- 다른 클래스로부터 상속을 받지 않는 모든 클래스는 자동적으로 Object클래스로부터 상속받는다.
class Tv{
...
}
- 위의 코드를 컴파일링하면 자동적으로 extends Object를 추가하여 Object로부터 상속받도록 한다.
class Tv extends Object{
...
}
→따라서 모든 클래스들은 Object클래스의 멤버들을 상속받기 때문에 Object클래스에 정의된 멤버들을 사용할 수 있다.
- toString()이나 equals(Object o)와 같은 메서드를 따로 정의하지 않고 사용할 수 있었던 이유가 이 메서드들이 Object 클래스에 정의된 메서드들이기 때문이다
'Java > Java 스터디' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Chapter 06. 객체지향 프로그래밍 I (part 4~6) (1) | 2023.03.13 |
|---|---|
| Chapter 06. 객체지향 프로그래밍 I (part 3) (1) | 2023.02.22 |
| Chapter 06. 객체지향 프로그래밍 I (part 1~2) (0) | 2023.02.21 |
| Chapter 05. 배열 (0) | 2023.02.15 |
| Chapter 04. 조건문과 반복문 (0) | 2023.02.15 |
